What is a U-Bolt and how do you measure them?
U-Bolts
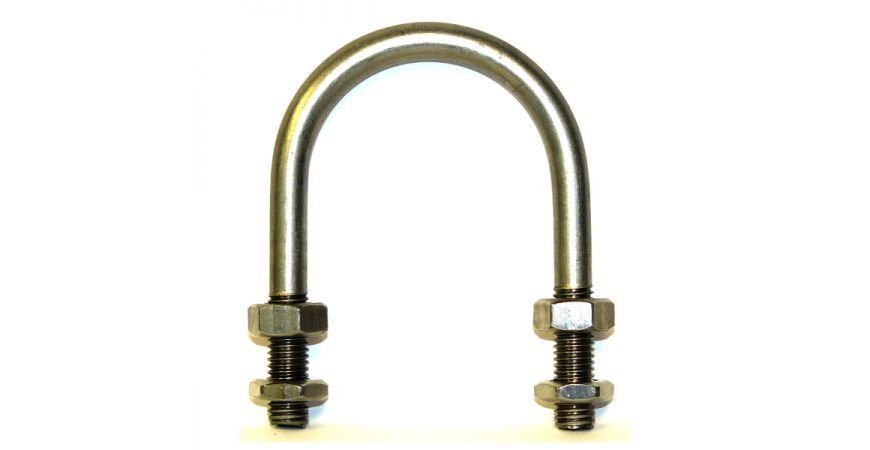
U-Bolts are probably the most common type of pipe support. A length of round threaded bar which is bent into a “U” shape with the primary purpose of fastening a pipe or tube to a surface. Though because of the very simple design, it can be used for a multitude of other purposes.
Trying to determine the correct size u-bolt for your application can be a daunting task. Part of this is to do with old pipework engineering speak. U-bolts are traditionally used to clamp pipes into place. Pipes are tubes and engineers who design pipe systems are wholly concentrated on the inside of the tube – because from there they can determine how much fluid or gas can flow through the pipe.
Makes sense – for them. So they will ask for a u-bolt to clamp a “50 nominal bore pipe” which means “Please can I have a U-bolt that will hold a pipe that has an inside diameter of 50 mm” (Not strictly accurate, but close for our purposes). Now, a British standard pipe with 50 mm inside diameter will have a 60.3 mm outside diameter. So “Please can I have a U-bolt that will hold a pipe that has an inside diameter of 50 mm” actually means “Please can I have a U-bolt that will hold a pipe that has an outside diameter of 60.3 mm”
Still with us? So to hold that 50 Nominal bore pipe needs a u-bolt that has between 65 and 70 mm depending on how much clamping is to take place. This is why traditionally, u-bolts are labelled the way they are – in Nominal Bore – all very frustrating for non-pipework engineers
Graphskill SUMS (GSUMS)
So step forward Graphskill SUMS, the new and best way to measure a u-bolt. Using this diagram we can see the key elements:
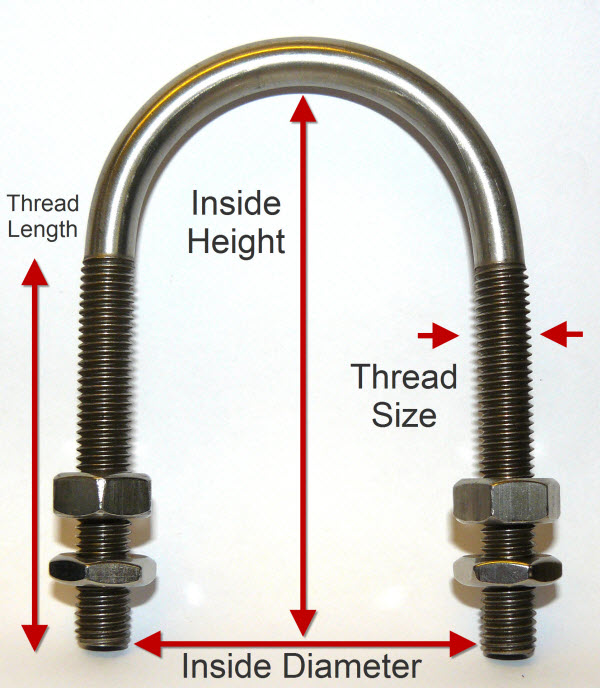
Graphskill SUMS: U-bolt
- Material/finish
- Thread size/bar Diameter
- Thread Length
- Inside Diameter (Distance between the legs)
- Inside height
Those five qualities will uniquely define any u-bolt and Graphskill are now utilising that in our naming conventions
Old Convention: T304 Stainless Steel 50 Nominal Bore British Standard gripping u-bolt (Only the dedicated expert will understand that)
New Convention: U-Bolt M10 *35mm Thread, 65mm Inside Diameter, 96mm Inside Height T304 Stainless Steel
Anyone should be able to read that and know if it will suit their needs
So for example:
Thread Size=M
Inside Diameter=D
Inside Height=H
Thread Length=T
Graphskill SUMS= UBOLT/MATERIAL/M*D*H*T
Example: UBOLT/GALV/M6*34*75*20
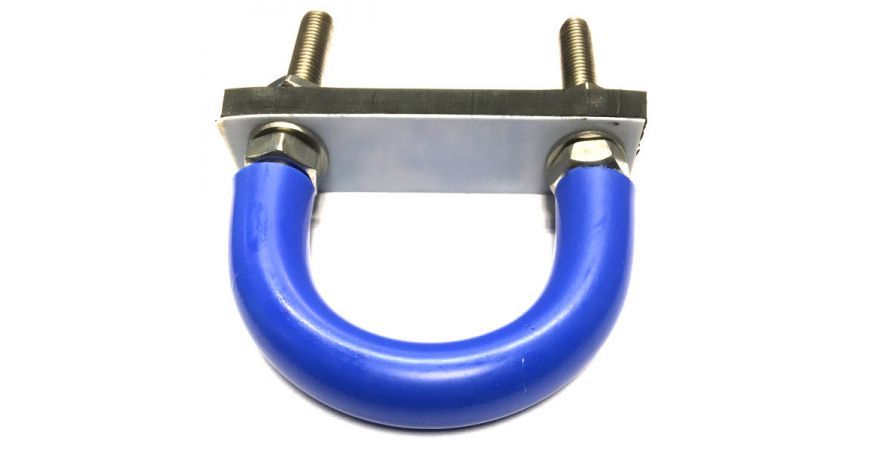
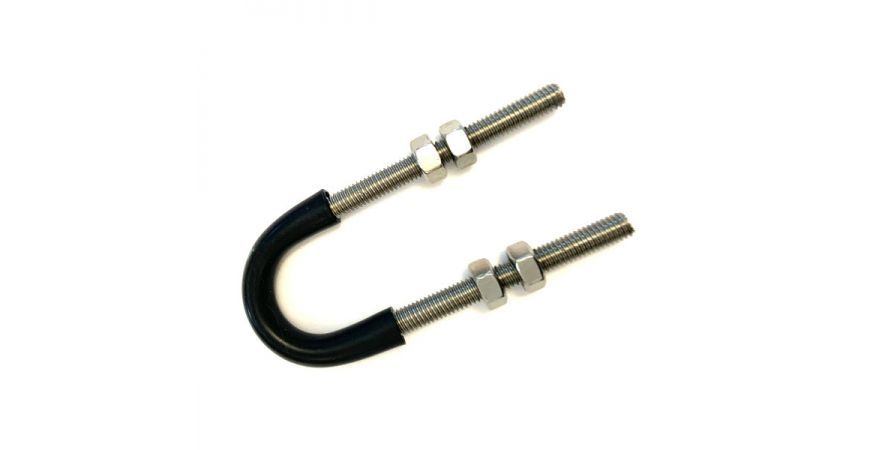
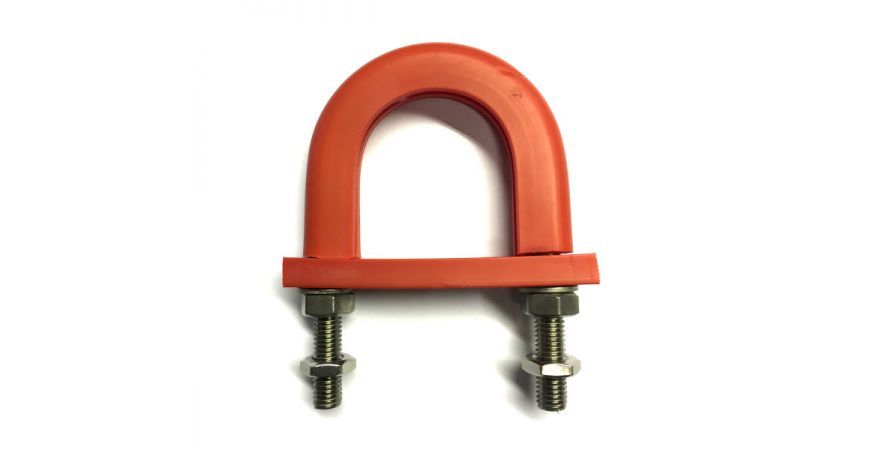
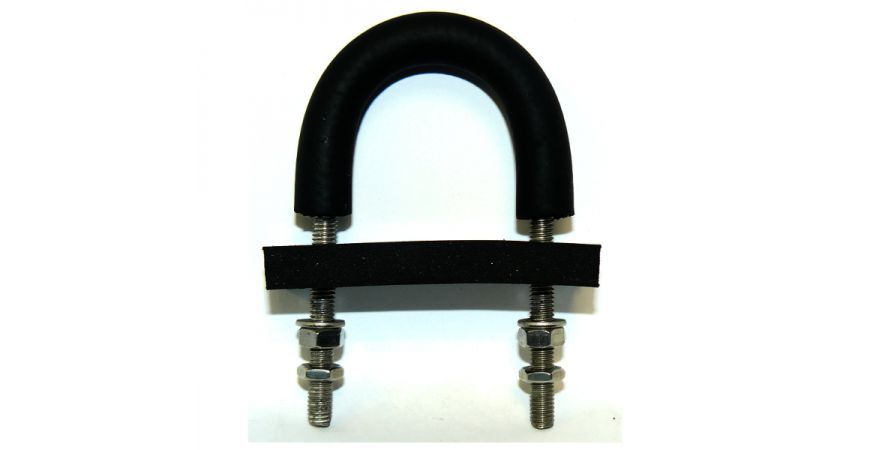
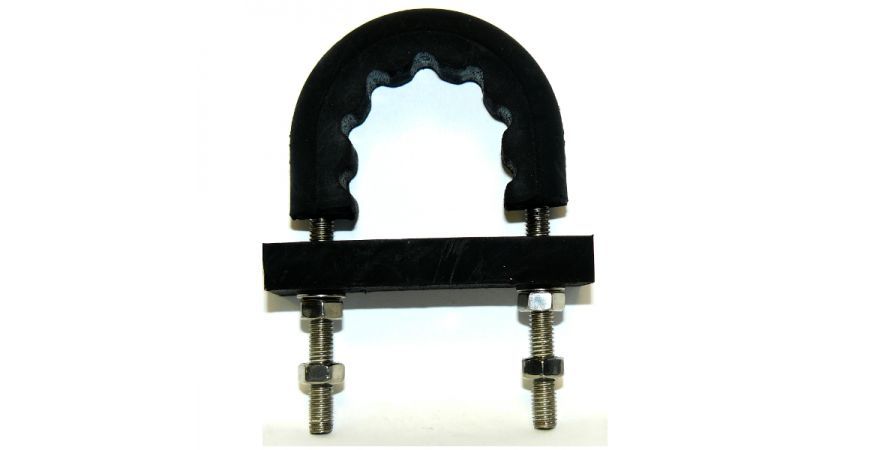
As already mentioned there are many styles of u-bolts. Sometimes you want to grip a pipe tightly, sometimes you want to loosely hold the pipe (perhaps to allow for thermal expansion, sometimes you need extra leg length perhaps to go through a wall. Then there are rubberised u-bolts for isolation, or low friction, or flame retardant. The list goes on - and you can see some of them shown below and on the slide show at the top of this post. To see our full range click here: U-bolts at Graphskill







